Many innovations in the field of artificial intelligence capture people’s attention as much as Generative AI. It’s the man behind the curtain, the invisible force that drives the creative machinery that generates text, music, and other artistic mediums. However, what is generative AI precisely, and how does it do its entrancing magic? Let’s explore this fascinating technology’s depths and solve its riddles.
What is Generative AI?
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a class of algorithms that can produce new content on their own that is similar to the input data they were trained on. Generative models can produce unique results by learning the underlying patterns and structures of the data they are exposed to, in contrast to typical AI systems that rely on predetermined rules and organized data. They may create a vast range of information with this capacity, including natural language writing and realistic visuals and musical creations.
The Key Players: GANs, VAEs, and More
Several fundamental designs, each with a unique method for generating new ideas, form the basis of generative artificial intelligence. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are one of the most well-known and effective among them. GANs are made up of two neural networks that are locked in a competitive dance: a discriminator and a generator. While the discriminator tries to discern between produced and actual samples, the generator creates synthetic data. Because of this adversarial training process, GANs are able to generate extremely realistic outputs that are identical to real data.
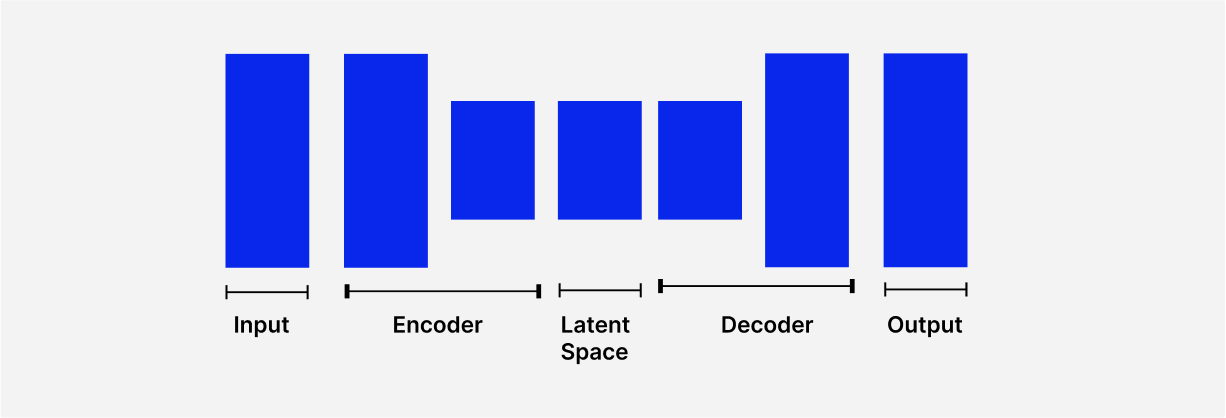
VAEs or Variational Autoencoders, provide an alternative viewpoint on generative modeling. VAEs acquire the ability to encode input data into a latent space of lower dimensions, from which they can create and modify new samples. VAEs produce a variety of outputs by sampling from this latent space while maintaining the fundamental qualities of the original input.
The Magic Unveiled: How Generative AI Works
Fundamentally, generative AI works by figuring out the input data’s underlying probability distribution. Generative models then produce fresh samples that closely mirror the training data by comprehending the statistical patterns and correlations within the data. Large volumes of data are used to train the model, which is then refined using iterative optimization techniques and advanced loss functions to direct the learning process.
Applications Across Industries
Numerous businesses have embraced generative AI, which is transforming areas like art, design, entertainment, and healthcare. Generative models are utilized in the fields of art and design to explore new design areas, produce visually attractive artworks, and facilitate the creative process. AI-generated literature, music, and video material is expanding the parameters of storytelling and innovation in the entertainment industry. Furthermore, generative models are used in healthcare to find new drugs, analyze medical images, and provide individualized treatment plans.
Conclusion
Generative AI holds the promise of unlocking new realms of creativity and innovation, challenging our perceptions of what machines can achieve. By understanding the principles and techniques behind generative modeling, we can demystify the magic and harness its transformative potential across various domains. As we continue to explore the frontiers of artificial creativity, Generative AI will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of human-machine collaboration.




